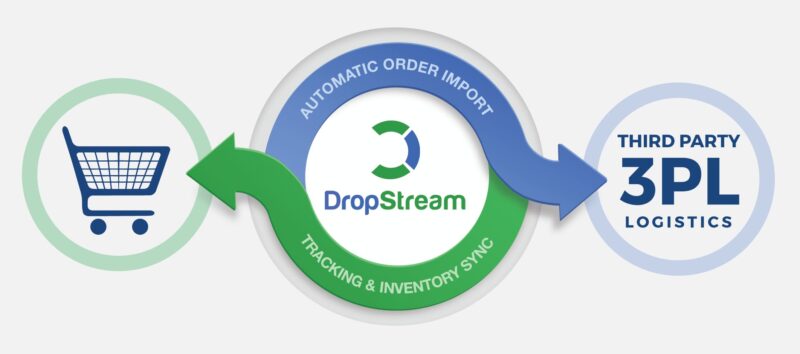
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the digital exchange of business information through standardized, electronically formatted documents between business partners. In this method, automation replaces paper documents and manual business processes to streamline incoming and outgoing document types like purchase orders, advance ship notices, and invoices.
Most Electronic Data Interchange transactions start by creating an electronic document, based on information from your business system(s), spreadsheets, or related transactions. These documents use standardized EDI formats, called transaction codes, for easy ingestion and use by many businesses.
Different providers use different EDI networks and systems to deliver electronic documents. There are several types of EDI solutions as well, ranging from web EDI portals, to direct EDI, to fully integrated EDI.
Key components of EDI
A complete EDI system consists of four components,
- EDI translation software, which converts the raw EDI data into a human-readable document or other meaningful format.
- EDI mapping software, which enables you to properly format EDI transactions being sent to your trading partner(s), as well as seamlessly import and export data from EDI transactions to and from your accounting or ERP system.
- Secure connectivity with your trading partners to transmit and optionally encrypt EDI transactions, either via the Internet or over a proprietary data network or transaction gateway (called a Value Added Network or VAN). This network should support whatever connectivity protocols you need, such as AS2 software, HTTPS, FTP and/or VAN interconnects.
- Customer and technical support to keep your business-critical EDI platform running smoothly 24×7.
How to choose the right EDI operating model
EDI software can be operated on-premises, in the cloud or via the Internet as WebEDI.
EDI solution on-premises (in-house operation)
With an on-premises solution, the company acquires the EDI software and operates it in its own data center, i.e. on its in-house or self-managed hardware. Operation and support are usually also carried out under the company’s own responsibility, but can also be outsourced to a hosting partner. The advantage of an on-premises solution is that all EDI requirements can be implemented without dependence on external partners.
EDI as a Cloud Service
With cloud services, IT operations can be outsourced to external service providers. Data, software, platforms or even computing power are outsourced to the cloud provider and used via the Internet. EDI can also be booked as a cloud service. With this operating model, the investment in an EDI software is completely unnecessary; instead, the most standardized EDI cloud service of a service provider is used.
WebEDI as an alternative for small and medium-sized enterprises
In order to operate EDI in the classical sense, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with low message volumes often lack the know-how. At the same time, in many cases there is no economic justification whatsoever for this. A further hurdle can be the technical connection to the internal ERP system. WebEDI enables you to receive, record and send EDI-based messages to your business partners partially automatically via electronic forms using a web browser over the Internet.
Contact Taksa for your Outsourcing Development Project requirements and see how our developers incorporate the best scalable application framework and technologies into your project.